Structure-Based Design of Potent and Orally Active Isoindolinone Inhibitors of MDM2-p53 Protein–Protein Interaction
Multi-faceted paper from the team at Astex Pharmaceuticals (UK) and Cancer Research UK Newcastle Drug Discovery Unit describing the rational design of novel isoindolinone inhibitors of the p53-MDM2 protein-protein interaction.
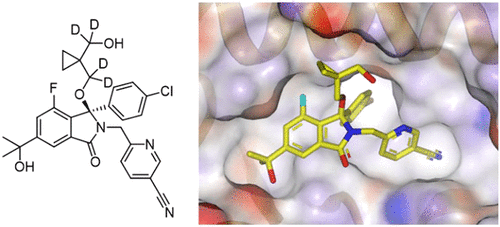
What’s particularly interesting was the application of deuterium to alleviate oxidation at a metabolic hot spot as well as reducing intestinal CYP3A4 metabolism to maximize oral bioavailability.
Also worth pointing out was the early replacement of a methyl of the t-butyl group with a hydroxyl group which maintained the desired Try67 OUT conformation while forming a favourable H-bond with Gln72. As a bonus, the substitution also introduced a less lipophilic and more drug-like substituent into the molecule.
Reference
Structure-Based Design of Potent and Orally Active Isoindolinone Inhibitors of MDM2-p53 Protein–Protein Interaction
Gianni Chessari, Ian R. Hardcastle, Jong Sook Ahn, Burcu Anil, Elizabeth Anscombe, Ruth H. Bawn, Luke D. Bevan, Timothy J. Blackburn, Ildiko Buck, Celine Cano, Benoit Carbain, Juan Castro, Ben Cons, Sarah J. Cully, Jane A. Endicott, Lynsey Fazal, Bernard T. Golding, Roger J. Griffin, Karen Haggerty, Suzannah J. Harnor, Keisha Hearn, Stephen Hobson, Rhian S. Holvey, Steven Howard, Claire E. Jennings, Christopher N. Johnson, John Lunec, Duncan C. Miller, David R. Newell, Martin E. M. Noble, Judith Reeks, Charlotte H. Revill, Christiane Riedinger, Jeffrey D. St. Denis, Emiliano Tamanini, Huw Thomas, Neil T. Thompson, Mladen Vinković, Stephen R. Wedge, Pamela A. Williams, Nicola E. Wilsher, Bian Zhang, and Yan Zhao.