Scale-up of PolyCYP reactions
Once a target metabolite or oxidised derivative has been synthesised by one or more PolyCYPs enzymes in the screening kit, a scale-up reaction with the best performing isoform is performed in order to access mg amounts of material for MetID and biological testing. The quickest and most cost-effective route for generating low mg amount of product is through the use of scale-up vials. Higher amounts of product can be generated using either a recombinant E.coli cell paste or through fermentation of a recombinant streptomyces clone expressing the isoform responsible for the biotransformation.
In this client case study, milligram amounts of specific oxidised products of two compounds were required. Both screening and scale-up reactions were conducted by Hypha for the client and the extract provided to the client for purification. Scale-up reactions were performed using 500 ml of disrupted E.coli cell pellet of PolyCYPs 196 and 152, dosed at 100 mg/L substrate, formulated with a cyclodextrin. Both reactions resulted in >50% turnover of the substrate. PolyCYPs reactions were also compared with biotransformations achieved from exposing the substrate to a panel of 16 wild type microbes, proven to be talented at metabolising a wide variety of drug compounds.
Clean background
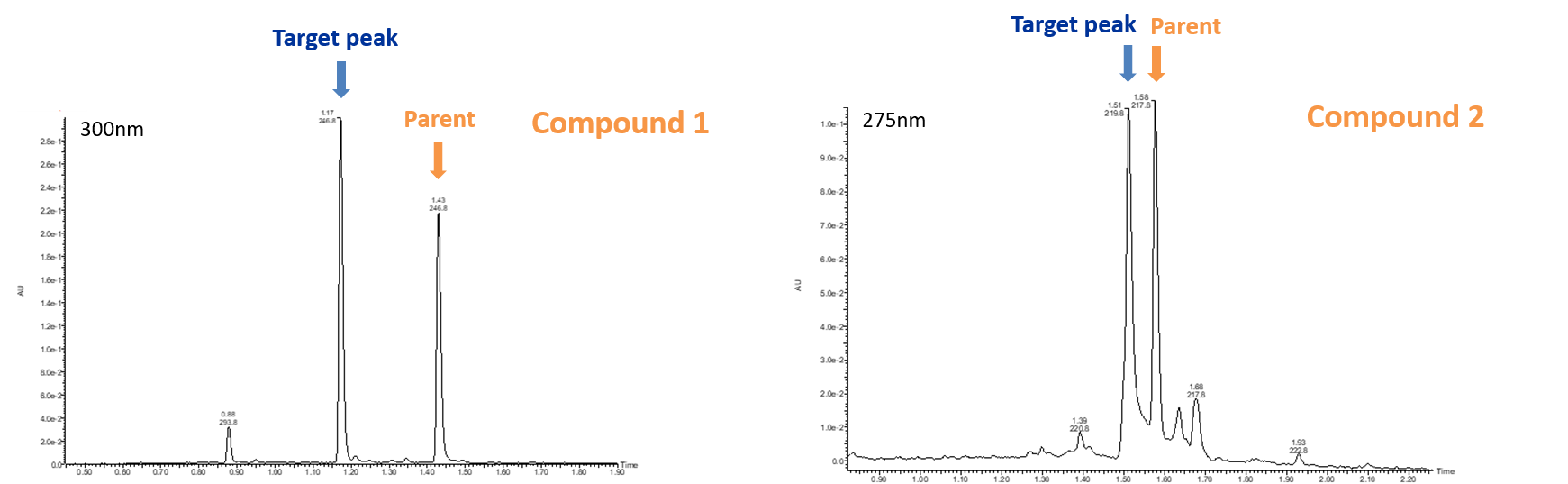
The target metabolite was produced in a “clean background” by PolyCYP 196, making purification straightforward.
Targeted production
Further and competing metabolism occurred in the whole cell microbial route, including production of glucuronides and a further oxidised metabolite.
For compound 1, several monohydroxylated metabolites were formed with the cleanest biotransformation to the target product achieved by PolyCYP 196. For compound 2, a single monohydroxylated target product was produced by PolyCYPs enzymes only, with PolyCYP 152 giving the best conversion. Other minor products were also of interest.
Related Resources
Introducing oxygen into a drug candidate late in the optimisation process has several applications including exploration of SAR (structure-activity relationships) and the ability to access derivatives that may possess superior properties such as improved metabolic stability and LLE (ligand-lipophilicity efficiency). Biocatalysis can provide access to chemical space in a complementary manner to chemical synthesis and provide a “one-experiment” solution to accessing multiple derivatives in parallel. This poster illustrates the application of a new biocatalysis kit, PolyCYPs®, to enable parallel synthesis of hydroxylated derivatives of drugs.
Access a brochure on Hypha’s PolyCYPs+ kits. The kits contain 20 enzymes effective for producing a wide range of phase 1 metabolites. As well as 18 PolyCYPs enzymes, the kit also contains human aldehyde oxidase (AOX1) and the main human hepatic flavin-containing monooxygenase (FMO3), with other human FMO isoforms also available from Hypha.
In this case study at least 2 mg of a monohydroxylated metabolite (M4), originally observed in rat liver microsomes, was required by a US pharma company. Using PolyCYPs, the target metabolite was supplied to the client together with a Certificate of Analysis within 22 days from receipt of order, exemplifying the short timelines achievable using PolyCYPs to access CYP-derived metabolites.