What We Do
Specialists in the synthesis, purification and characterisation of drug and agrochemical metabolites, API degradates, and natural products
Your trusted partner in pharmaceutical and agrochemical R&D
Hypha Discovery is a specialist CRO supporting pharmaceutical and agrochemical companies worldwide. We are experts in:
Scalable synthesis, purification and identification of drug metabolites
Production of late-stage oxidised derivatives of lead compounds
Synthesis, purification and identification of manufacturing impurities and degradation products
Production, purification and structure elucidation of natural products, including strain improvement
NMR Spectroscopy and Structure Elucidation
NMR Spectroscopy and Structure Elucidation
• Quantitative NMR
• Interpretation and documentation of spectra
Our Metabolite Expertise
Hypha’s One-Stop Metabolite Shop
We offer a comprehensive suite of techniques – Hypha’s One Stop Metabolite Shop – for provision of even the most difficult-to-synthesise metabolite. We use chemical synthesis, microbial biotransformation, recombinant enzymes such as PolyCYPs, and mammalian liver and other tissue fractions. We are also experts in purification of metabolites from biological matrices, and structure elucidation by cryoprobe NMR.
Our strategy allows production of phase 1 and 2 metabolites from microgram scale for definitive MetID, and up to multi mg / gram scale for further biological evaluation and provision of certified bioanalytical standards.
We also provide a service to access gut metabolites using human faecal incubations performed under anaerobic conditions.
Chemical Synthesis
Late-stage chemical glucuronidation
Mammalian biotransformation
Panels of liver S9s / microsomes
Microbial biotransformation
Proven panels of bacteria and fungi
Purification & structure elucidation
COAs, acquisition / interpretation of NMR data
Recombinant enzymes
PolyCYPs, hrCYPs, AOX, FMOs
Our Products
Hypha has developed several recombinant enzyme products that can be accessed, either for use in your own lab, or by contracting Hypha to do the testing
To access phase I drug metabolites, Hypha has key enzymes including a set of proprietary diverse microbial CYPs called PolyCYPs®, as well as human recombinant aldehyde oxidase (AOX1) and all five human isoforms of flavin monooxygenase (FMOs). Each enzyme is cloned into E.coli and validated against a panel of relevant drug substrates to demonstrate utility.
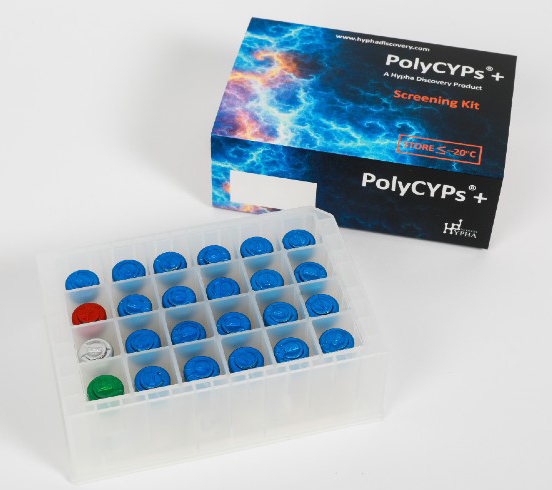
A set of 18 PolyCYPs enzymes, AOX1 and FMO3 are available in a kit form called PolyCYPs+. PolyCYPs can also be used as an effective tool to expand the medicinal chemistry toolbox to access late-stage oxidised derivatives of drugs. Hydroxylation has been identified by scientists as “a key tactic to consider as part of a late-stage functionalization strategy” (Bostrom et al., 2018). PolyCYPs can address this need by providing a fast and easy way to hydroxylate aliphatic or aromatic moieties at multiple sites in parallel.
PolyCYPs kits
PolyCYPs+ kits are simple to use. They contain all co-factors needed to screen a drug substrate for oxidised metabolites, as well as a control compound and formulant for poorly water-soluble test compounds.
In addition to the enzymes supplied in PolyCYPs+ kits, Hypha also offer a service to screen compounds against any of our recombinant enzymes, including all five human FMO isoforms.
All recombinant enzymes are fully scalable to provide larger quantities of metabolites. Scale-up vials of PolyCYPs+ enzymes are available, as well as the ability to scale-up large quantities of metabolites at Hypha as a service offering. We can also undertake purification and structure elucidation of metabolites by NMR spectroscopy.

Publications
Read about our publications in the fields of metabolite synthesis, biotransformation and natural products chemistry
Brochures
Access brochures on drug metabolite synthesis, Hypha’s one-stop metabolite shop and the PolyCYPs platform
Ready to begin? Our scientists are available to talk through your requirements
Hypha Discovery is a UK-based CRO supporting pharmaceutical and agrochemical companies worldwide through the production of metabolites and new derivatives of drugs and agrochemicals in discovery and development.
Resources
Cookie Policy | Privacy Policy | Website Terms and Conditions
© Hypha Discovery 2021. All Rights Reserved. Website by Fifteen.co.uk