Case Studies
Case Studies and Client Projects
Latest Case Studies
We have extensive experiences in synthesising glucuronides using either scalable biotransformation or proprietary late-stage chemical methods.
Hypha can monitor stability of drugs or their metabolites including stability and biotransformation of drugs in a faecal environment.
We are used to fishing out and purifying compounds that constitute only a small % of a sample, such as in this case study where four manufacturing batch impurities were isolated and identified.
In this case study we look at how Hypha make deuterated metabolites, illustrated using case studies where biotransformation and late-stage chemical synthesis techniques were employed.
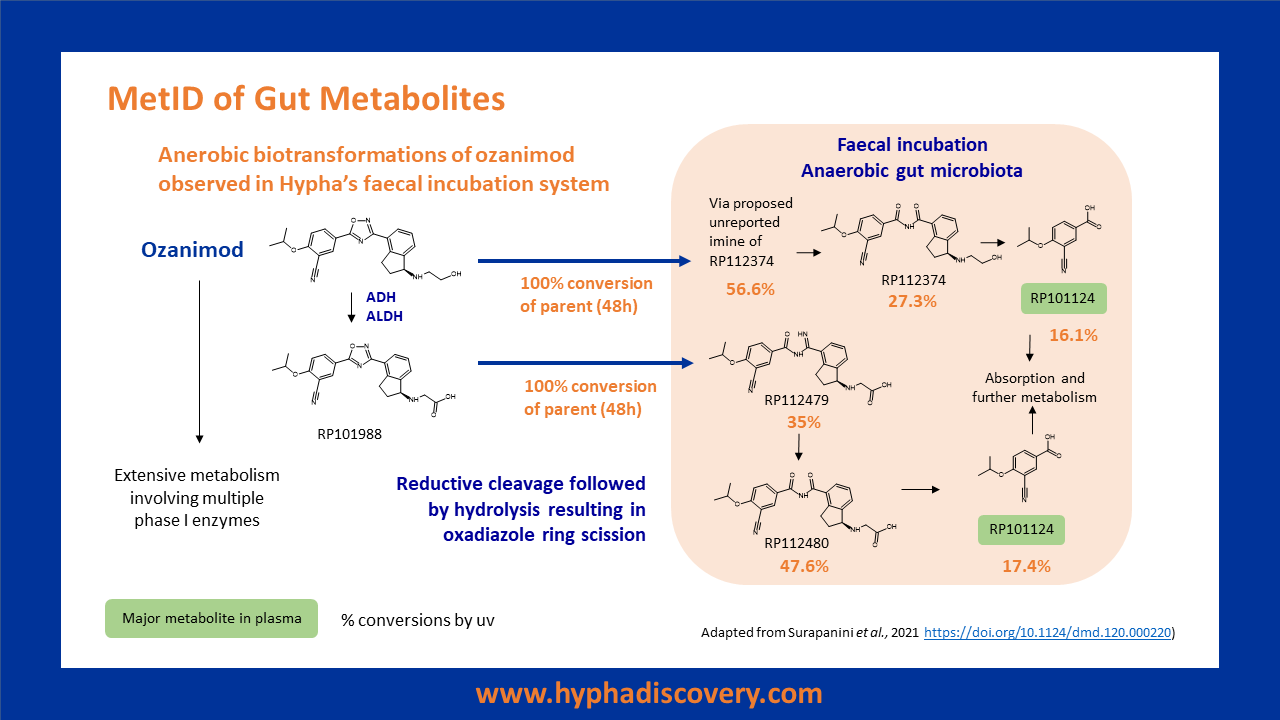
Hypha’s human faecal pool can be used to screen for reduced metabolites of drugs, as exemplified with sulfasalazine and nizatidine.
Hypha have designed a set of late-stage chemical oxidation conditions, resulting in a toolbox for the synthesis and identification of API degradation products.
PolyCYPs were used effectively to produce a hydroxylated metabolite of OSA821, a lead compound in the Open Source Antibiotics (OSA) diarylimidazole series.
Formation and scale-up of human metabolites formed through mixed metabolic pathways is possible using Hypha’s microbial biocatalysis system. In vivo human metabolism of Incyte’s IND epacadostat (EPA) forms 3 major circulating metabolites, from both primary and secondary pathways. Glucuronidation of EPA forms M9, the dominant metabolic pathway, in conjunction with formation of an amidine M11 and an N-dealkylated metabolite, M12.
Hypha’s microbial biocatalysis process is effective at generating metabolites at up to gram scale. Through Hypha and Selcia’s partnership, [13C], [14C], [2H], [3H] and [15N]-labelled metabolites can be accessed to support regulatory, development or research projects in the pharma and crop protection industries. Hypha establishes optimized processes using unlabelled or stable labelled parent substrates, which can then be transferred to Selcia’s state-of-the-art radiochemistry labs for the production of radiolabelled metabolites.
Stay up to date with the latest news from Hypha Discovery
Sign up for our quarterly newsletters and monthly "Metabolite Tales" blog
Ready to begin? Our scientists are available to talk through your requirements
Hypha Discovery is a UK-based CRO supporting pharmaceutical and agrochemical companies worldwide through the production of metabolites and new derivatives of drugs and agrochemicals in discovery and development.
Resources
Cookie Policy | Privacy Policy | Supplier Code of Conduct Policy | Website Terms and Conditions
© Hypha Discovery 2021. All Rights Reserved.