What We Do
Manufacturing and Degradation Impurities
Manufacturing and Degradation Impurities
Identification of drug substance impurities
Hypha have extensive experience in purifying compounds present in small amounts in samples. If you have impurities or degradation products in your manufacturing batch or shelf-life study samples, we can purify and identify the material. We use high field micro cryoprobe NMR spectroscopy to elucidate the structures of compounds, meaning only small amounts need to be isolated for full identification. Typically we acquire 1H, 13C, COSY, HSQC, HMBC and NOESY NMR spectra to provide fully annotated structural data.
A unique toolbox for the synthesis of degradation products
We have designed a set of late stage chemical oxidation conditions, resulting in a toolbox for the synthesis and identification of API degradation products and impurities. These also include electrochemistry and photochemistry methods.
The suite of techniques to produce and identify degradation products is widened by:
- Expertise in biotransformation
- Purification of multiple products from shelf-life studies
- Identification from micrograms of pure material using cryoprobe NMR
Pure material can be supplied for analytical method development, quantification and safety evaluations, along with Certificates of Analysis.
Chemical Oxidation Screen
Hypha’s chemical oxidation screen creates oxidised products using multiple diverse conditions. Broad oxidation chemistry has been incorporated through a comprehensive evaluation of the literature and in-house knowledge, with the inclusion of both peroxide and radical reagents. The screen has been validated with a set of structurally diverse substrates.
Following a quick optimization step, reactions can be scaled to make milligram to gram quantities of the degradation product. Multiple products can be isolated from complex mixtures and structures elucidated.
What We Do
Why access degradation products?
The safety of a drug is impacted by it’s susceptibility to form degradation products. To meet regulatory guidelines, significant API degradation products and drug substance impurities must be identified. This involves isolation and definitive structure elucidation of the degradate, typically by NMR spectroscopy. In addition, pure material is needed for determining the relative response factor (RRF) of the degradate compared to the API, so that the weight % formation of degradation products can be accurately calculated. Pure degradates may also be required for use as analytical standards, or for safety assessments.
Oxidative degradation pathways commonly result in the most complex reaction profiles, highlighted by Nanda and colleagues who state that, “…faster and practical ways of enriching an API with relevant oxidative degradates and their isolation in pure form is highly desirable.” Thus, availability of an oxidation toolkit incorporating broad chemistry, is beneficial for rapidly generating oxidised products.
Ref: Nanda et al., 2019. Enrichment of Relevant Oxidative Degradation Products in Pharmaceuticals With Targeted Chemoselective Oxidation. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 108, 4, 1466-1475.
Manufacturing and Degradation Impurities - Services at Hypha
Rapid generation of diverse oxidised products to understand an API's oxidative sensitivity
Backed up by biotransformation options e.g. microbes, PolyCYPs, other enzymes e.g. laccase
Purification from shelf life study samples and manufacturing batches
Structure elucidation by cryoprobe NMR
Case Studies
Identification of Fluoxetine Storage Impurities
Hypha purified and identified two sucralose conjugates of fluoxetine, formed during a study where the drug had been stored at 50oC for 2 months. Simulation of the reaction at 50oC for 7 days permitted purification and identification of two sucralose conjugates. Subtle differences in the NMR spectra revealed the presence of stereoisomers resulting from the reaction of sucralose with racemic fluoxetine.
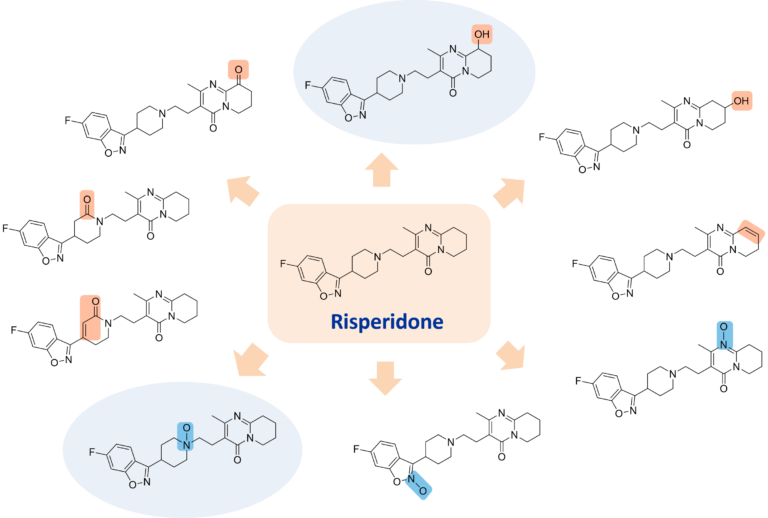
Tomar et al. report that the two major degradants formed from risperidone are an N-oxide and 9-hydroxy risperidone (also known as paliperidone, the primary active metabolite of rispiridone sold at Invega).
Risperidone was screened against a diverse set of oxidation conditions and the products analysed by LC-MS. Reactions in which oxidation products were observed were scaled up, resulting in the isolation of 10 different oxidation products. Structures were elucidated through use of cryoprobe NMR.
Both the N-oxide and 9-hydroxy risperidone major degradation products were produced (shaded) along with 8 other oxidised derivatives.
Ref: Tomar et al., 2004. Identification and characterization of major degradation products of risperidone in bulk drug and pharmaceutical dosage forms. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 36, (1), 231-235
Resources
Explore our library of resources comprising brochures, case studies, posters and publications about the work we do.
Hypha have designed a set of late-stage chemical oxidation conditions, resulting in a toolbox for the synthesis and identification of API degradation products.
Introducing oxygen into a drug candidate late in the optimisation process has several applications including exploration of SAR (structure-activity relationships) and the ability to access derivatives that may possess superior properties such as improved metabolic stability and LLE (ligand-lipophilicity efficiency). Biocatalysis can provide access to chemical space in a complementary manner to chemical synthesis and provide a “one-experiment” solution to accessing multiple derivatives in parallel. This poster illustrates the application of a new biocatalysis kit, PolyCYPs®, to enable parallel synthesis of hydroxylated derivatives of drugs.
If clearance mechanisms of the test drug results in sufficient quantities of the major metabolites in biological material such as faeces or urine, purification and subsequent identification of metabolites from such matrices is possible. One such project undertaken at Hypha resulted in tens of milligrams of the R- and S-O-glucuronides of carisbamate, a neuromodulator developed by SK Life Science, which were purified to >95% purity from 150 ml of urine using a three-step purification method.
Find out about our other services

We worked with Hypha discovery to synthesize metabolites via a chemical approach in enough quantities for pharmacology studies for one of our products. Hypha has well understood our request and provided a very good quality of service in time, in quantity and quality with the needed level of regular communication. We will work certainly with them in the future and will recommend them.
Dr. Laure Navarre, Director Process Chemistry
Poxel, France
Ready to begin? Our scientists are available to talk through your requirements
Hypha Discovery is a UK-based CRO supporting pharmaceutical and agrochemical companies worldwide through the production of metabolites and new derivatives of drugs and agrochemicals in discovery and development.
Resources
Cookie Policy | Privacy Policy | Website Terms and Conditions
© Hypha Discovery 2021. All Rights Reserved. Website by Fifteen.co.uk