Identifying and Scaling up Aldehyde Oxidase Metabolites
Provision of multiple human metabolites via biotransformation
There has been a notable increase in metabolism of new drug candidates through non-CYP phase I pathways such as those mediated via aldehyde oxidase (AO).1 Further, mixed AO/P450 substrates may be subject to metabolic shunting, an important consideration during toxicology and DDI assessment of these drugs.2 Access to metabolites may thus be important to consider for drugs with mixed metabolism.
Increasing relevance of AO in drug metabolism
Medicinal chemistry strategies to reduce cytochrome P450-dependent metabolism have resulted in an increase in metabolism of new drug candidates through AO and other non-CYP enzymes
Metabolic shunting
Mixed AO/P450 substrates may be subject to metabolic shunting with consequent implications for DDIs if co-administered with a CYP inhibitor
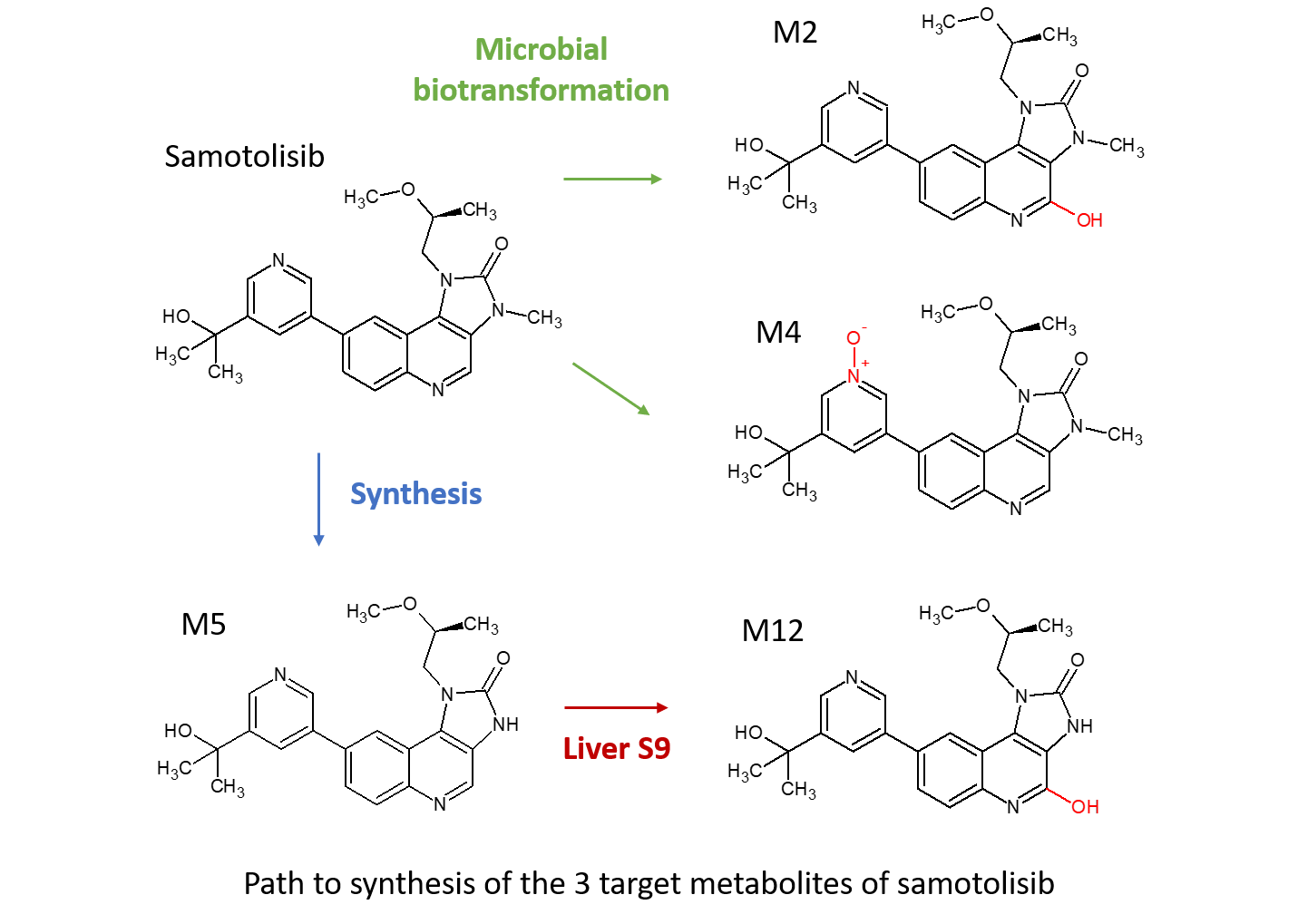
Zhou and colleagues at Lilly presented a poster at the 2018 ISSX meeting in Montreal on “Elimination of [14C]-LY3023414 by Aldehyde Oxidase and CYP Enzymes in Humans Following Oral Administration.” Both AO and CYP enzymes were responsible for the metabolic clearance of LY3023414 with the non-CYP enzymes mediating approximately half of the clearance of the drug. The predominant metabolic clearance pathways were aromatic hydroxylation of the quinoline moiety (M2), N-demethylation (M5) and quinoline oxidation with N-demethylation (M12).
No metabolism was observed when tested vs 5 human recombinant CYPs, however screening of LY3023414 against a subset of Hypha’s microbial biotransforming strains generated a number of metabolites. The best strain was scaled-up to 6L to access target metabolites M2 and M4. Subsequent incubation of the synthesised intermediate M5 vs Cyno S9 enabled production of a further target metabolite M12. Metabolites were purified to > 95% purity by Hypha and the structures confirmed by LC-MS and NMR. The AO mediated hydroxylated metabolite (M2, 20.1mg) and an N-oxide (M4, 66.3mg) were made via microbial biosynthesis and a CYP/AO mediated metabolite (M12, 18.4mg) was generated through liver S9 incubations. Use of combined biotransformation approaches can therefore enable access to metabolites created through different pathways, including AO and CYP mediated metabolites.
References
1. Rashidi & Soltani, 2017. Expert Opin. Drug Discov.12 (3), 305-316.
2. Crouch et al., 2016. Drug Metab Dispos 44, 1296-1303.
Related Resources
Hypha’s microbial biocatalysis process is effective at generating metabolites at up to gram scale. Through Hypha and Selcia’s partnership, [13C], [14C], [2H], [3H] and [15N]-labelled metabolites can be accessed to support regulatory, development or research projects in the pharma and crop protection industries. Hypha establishes optimized processes using unlabelled or stable labelled parent substrates, which can then be transferred to Selcia’s state-of-the-art radiochemistry labs for the production of radiolabelled metabolites.
In this case study at least 2 mg of a monohydroxylated metabolite (M4), originally observed in rat liver microsomes, was required by a US pharma company. Using PolyCYPs, the target metabolite was supplied to the client together with a Certificate of Analysis within 22 days from receipt of order, exemplifying the short timelines achievable using PolyCYPs to access CYP-derived metabolites.
In Chapter 4 of the book on “Identification and quantification of drugs, metabolites, drug metabolizing enzymes and transporters”, Hypha authors summarise the different methods employed for producing metabolites of drugs, illustrated with representative examples from the literature and work undertaken at Hypha. The chapter also includes a discussion and examples of the use of NMR spectroscopy for structure elucidation of metabolites.


