Resources
Publications
Publications
Metabolite identification is an integral part of both preclinical and clinical drug discovery and development. Synthesis of drug metabolites is often required to support definitive identification, preclinical safety studies and clinical trials.
Leishmaniasis is a Neglected Tropical Disease caused by the insect-vector borne protozoan parasite, Leishmania species. Infection affects millions of the World’s poorest, however vaccines are absent and drug therapy limited. Recently, public-private partnerships have developed to identify new modes of controlling leishmaniasis. Most of these collaborative efforts have relied upon the small molecule synthetic compound libraries held by industry, but the number of New Chemical Entities (NCE) identified and entering development as antileishmanials has been very low. In light of this, here we describe a public-private effort to identify natural products with activity against Leishmania mexicana, a causative agent of cutaneous leishmanaisis (CL).
According to the World Health Organization, more than 1 billion people are at risk of or are affected by neglected tropical diseases. Examples of such diseases include trypanosomiasis, which causes sleeping sickness; leishmaniasis; and Chagas disease, all of which are prevalent in Africa, South America, and India. Our aim within the New Medicines for Trypanosomatidic Infections project was to use (1) synthetic and natural product libraries, (2) screening, and (3) a preclinical absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion–toxicity (ADME-Tox) profiling platform to identify compounds that can enter the trypanosomatidic drug discovery value chain.
As part of an international research project, the marine fungal strain collection of the Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research (GEOMAR) research centre was analysed for secondary metabolite profiles associated with anticancer activity. Strain MF458 was identified as Tolypocladium geodes, by internal transcribed spacer region (ITS) sequence similarity and its natural product production profile.
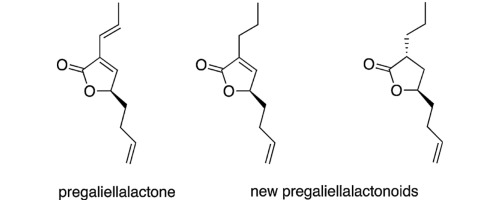
An extract of a culture of the fungus Galiella rufa yielded several new derivatives of pregaliellalactone (1) that were characterised by NMR and MS experiments. The tetraene 4 has been reported previously, but was in this investigation isolated in sufficient amounts for the determination of the configuration of the C-4/C-5 double bond which is Z, not E.
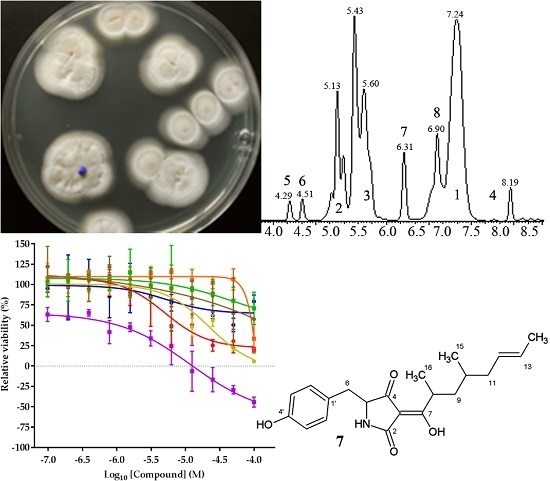
This study covers the isolation, testing, and identification of natural products with anticancer properties. Secondary metabolites were isolated from fungal strains originating from a variety of marine habitats. Strain culture protocols were optimized with respect to growth media composition and fermentation conditions. From these producers, isolated compounds were screened for their effect on the viability and proliferation of a subset of the NCI60 panel of cancer cell lines. Active compounds of interest were identified and selected for detailed assessments and structural elucidation using nuclear magnetic resonance.
Stay up to date with the latest news from Hypha Discovery
Sign up for our quarterly newsletters and monthly "Metabolite Tales" blog
Ready to begin? Our scientists are available to talk through your requirements
Hypha Discovery is a UK-based CRO supporting pharmaceutical and agrochemical companies worldwide through the production of metabolites and new derivatives of drugs and agrochemicals in discovery and development.
Resources
Cookie Policy | Privacy Policy | Website Terms and Conditions
© Hypha Discovery 2021. All Rights Reserved. Website by Fifteen.co.uk