Resources
Scientific posters
Posters
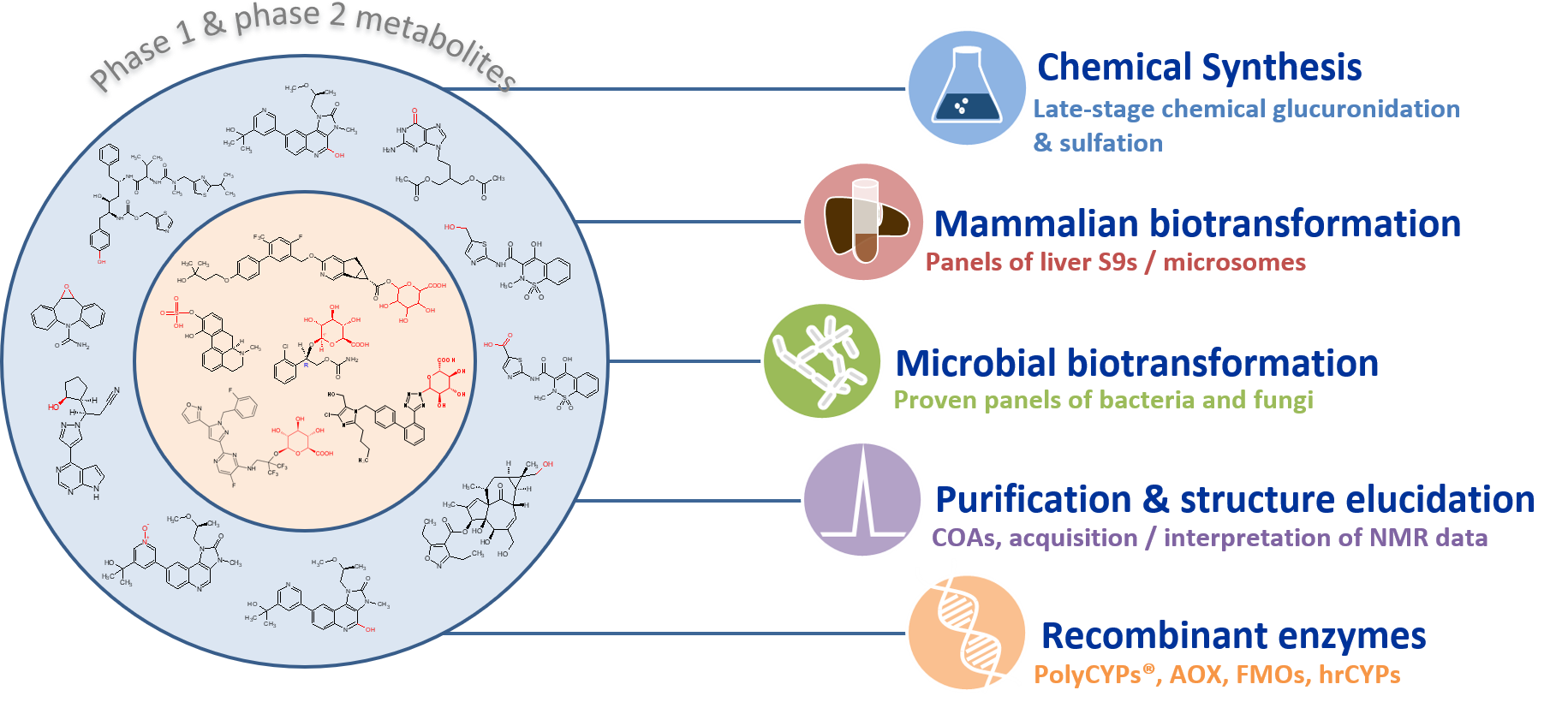
Often several strategies are needed to access all key metabolites observed during drug development programs. Hypha has developed a “one-stop metabolite shop” scheme, which utilizes a combination of biological and chemical techniques in order to fulfil requirements to access any type of metabolites. The one-stop metabolite concept offers a parallel or sequential screening step to identify the most productive and cost-effective method to produce target metabolites. Depending on the type and quantity of metabolite required, a combination of chemical synthesis, mammalian S9, microbial biotransformation and recombinant phase I enzymes can be employed. Once the optimal production system is identified, the method can be scaled up to provide up to tens of grams of purified metabolites.
Introducing oxygen into a drug candidate late in the optimisation process has several applications including exploration of SAR (structure-activity relationships) and the ability to access derivatives that may possess superior properties such as improved metabolic stability and LLE (ligand-lipophilicity efficiency). Biocatalysis can provide access to chemical space in a complementary manner to chemical synthesis and provide a “one-experiment” solution to accessing multiple derivatives in parallel. This poster illustrates the application of a new biocatalysis kit, PolyCYPs®, to enable parallel synthesis of hydroxylated derivatives of drugs.
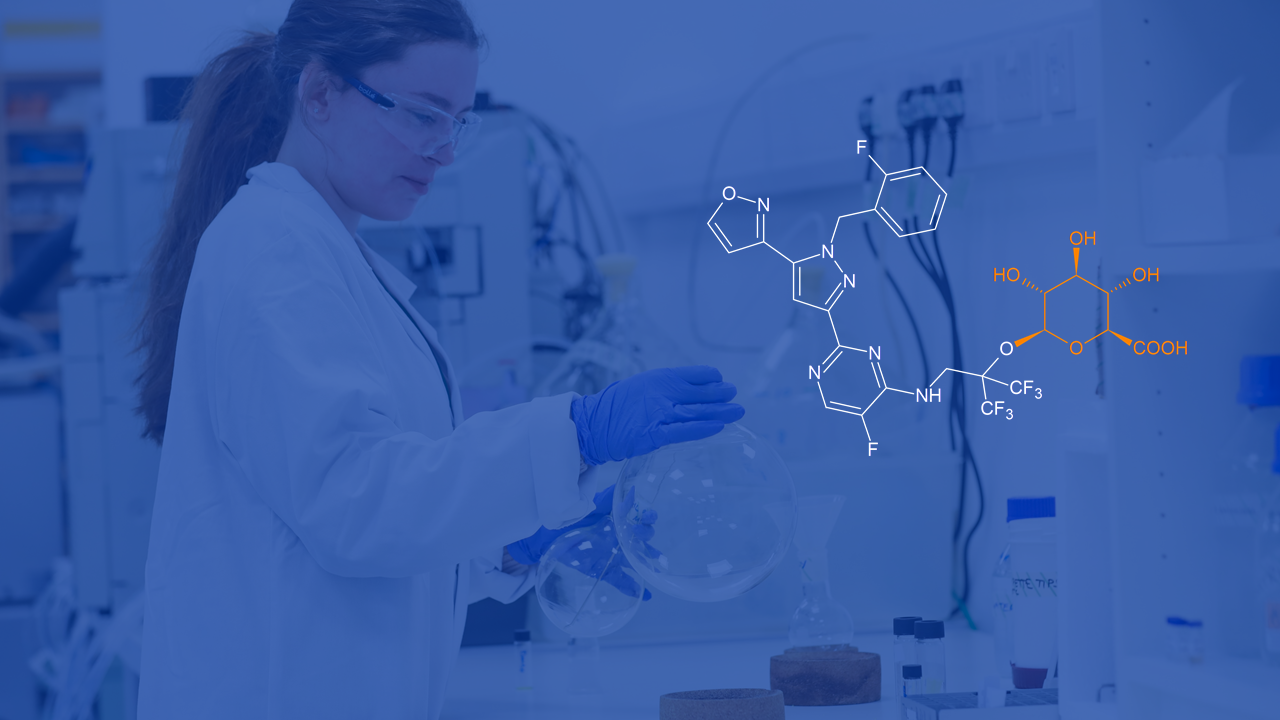
In recent years, FDA guidance has advised initiating human metabolite profiling earlier in drug development, emphasizing the importance of metabolite identification and quantification to evaluate a drug metabolite’s safety and pharmacological activity. Praliciguat (IW-1973) is a soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) stimulator in Phase 2 clinical trials for diabetic nephropathy and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). During studies on metabolism of praliciguat in preclinical species and in human hepatocytes, a prominent direct O-glucuronide metabolite was detected.
This poster illustrates the application of a new biocatalysis kit, PolyCYPs®, to enable scalable synthesis of CYP-derived metabolites of drugs. The PolyCYPs platform is comprised of a set of recombinant cytochrome P450 enzymes and redox partners cloned from some of the talented actinomycetes in Hypha’s biotransformation panel. Enzymes in the kit catalyze the oxidation of a wide variety of substrate types to generate multiple mammalian and microbial-derived CYP metabolites.
PolyCYP6, a functional bacterial Class I cytochrome P450, was successfully mined from one of Hypha’s actinomycete strains and converts the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug diclofenac into its hydroxylated human metabolites. Improvement of the PolyCYP cytochrome P450 cell factory for efficient whole-cell biotransformation was achieved through co-expression with specific redox partners and changing components of the T7 expression plasmid. The highest yielding recombinant strain expressed PolyCYP6 with the P. putida reductase system. An ampicillin resistant marker & high copy vector also further improved yields of hydroxylated products.
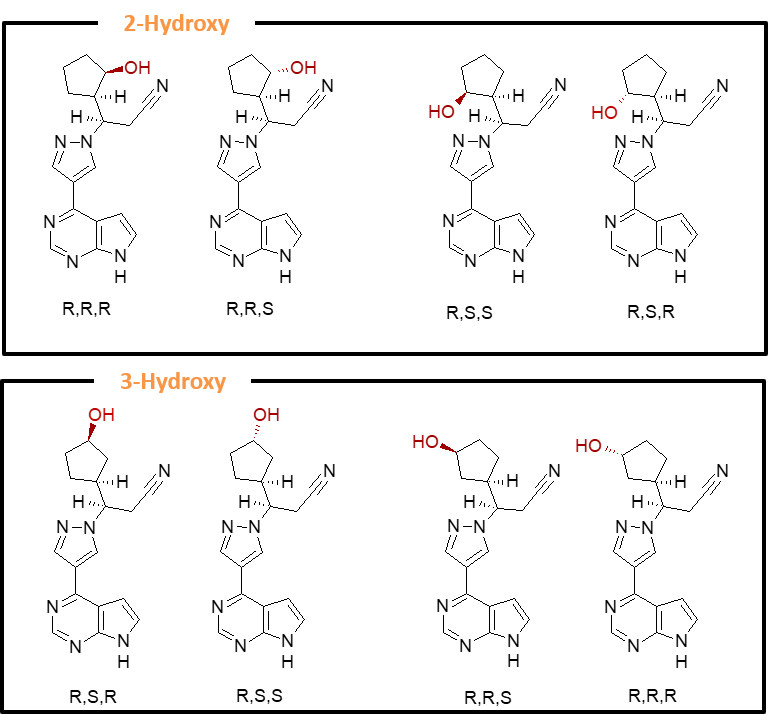
The first-in-class JAK inhibitor, ruxolitinib (trade names Jakafi® and Jakavi®), is primarily metabolized to a complex mixture of stereoisomeric cyclopentyl hydroxyl and keto metabolites. Application of Hypha’s microbial-based biocatalytic C-H bond activation to ruxolitinib resulted in the production of an array of hydroxylated and further oxidized keto metabolites, many of which corresponded to circulating human metabolites. All possible oxidized isomers of the aliphatic cyclopentyl moiety were derived from a variety of microbial species which were readily scaled up, enabling efficient production of stereoisomer metabolite standards for structural characterization and bioanalytical monitoring.
Stay up to date with the latest news from Hypha Discovery
Sign up for our quarterly newsletters and monthly "Metabolite Tales" blog
Ready to begin? Our scientists are available to talk through your requirements
Hypha Discovery is a UK-based CRO supporting pharmaceutical and agrochemical companies worldwide through the production of metabolites and new derivatives of drugs and agrochemicals in discovery and development.
Resources
Cookie Policy | Privacy Policy | Website Terms and Conditions
© Hypha Discovery 2021. All Rights Reserved. Website by Fifteen.co.uk